Yemen lost the title of Arabia Felix, or “Fortunate Arabia”, long ago. It has suffered civil wars, tribalism, jihadist violence and appalling poverty. But none of this compares with the misery being inflicted on the country today by the war between a Saudi-led coalition and the Houthis, a Shia militia backed by Iran.
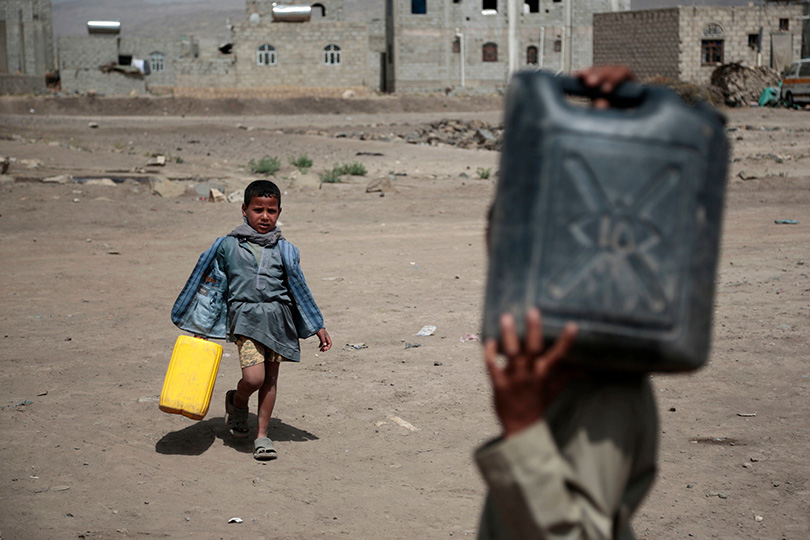
The UN reckons three-quarters of Yemen’s 28m people need some kind of humanitarian aid. Mounting rubbish, failing sewerage and wrecked water supplies have led to the worst cholera outbreak in recent history. The country is on the brink of famine. The economy has crumbled, leaving people with impossible choices. Each day the al-Thawra hospital in Hodeida must decide which of the life-saving equipment to run with what little fuel it has.
Perhaps the worst of it is that much of the world seems unperturbed, calloused by the years of bloodshed in Syria and other parts of the Middle East, and despairing of its ability to effect change. To be cynical, Yemen is farther away from Europe than Syria is; its wretched people do not, on the whole, wash up in the West seeking asylum.
Yet the world ignores Yemen at its peril. Set aside for a moment the obligation to relieve suffering and protect civilians. Hard security interests are also at stake. The world can ill afford another failed state—a new Afghanistan or Somalia—that becomes a breeding-ground for global terrorism. Yemen, moreover, dominates the Bab al-Mandab strait, a choke-point for ships using the Suez canal. Like it or not, the West is involved. The Saudi-led coalition is fighting with Western warplanes and munitions. Western satellites guide its bombs.
Slippery Saleh
Like so much else in the Arab world, Yemen’s agony can be traced to the Arab-spring uprisings of 2011. Mass protests, a near-assassination of the then president, Ali Abdullah Saleh, and a shove from neighbouring petro-states forced him to step down in 2012 in favour of his vice-president, Abd Rabbo Mansour Hadi. A draft constitution in 2015 proposed a federal system and a parliament split between northerners and southerners. But the Houthi rebels, who had fought Mr Saleh, rejected it. The Houthis, who follow the Zaydi branch of Shiism (as do perhaps 40% of Yemenis), complained that, among other things, the constitution stuck them in a region with few resources and without access to the sea.
Now allied with Mr Saleh, who spotted an opportunity for a comeback, the Houthis ousted Mr Hadi from Sana’a, the capital, and chased him all the way to Aden. Saudi Arabia gathered a coalition of Arab states and local militias—among them Islamists, Salafists and southern separatists—and forced the Houthis to retreat partway. For the past year, the battle-lines have barely moved. The Houthis are too weak to rule over Yemen but too powerful for Saudi Arabia to defeat.
As a result, Yemenis have become the pawns in the regional power-struggle between Saudi Arabia and Iran. Alarmed by Iran’s spreading influence, the Saudis have begun to speak of the Houthis rather as Israelis refer to the Lebanese militia, Hizbullah: a dangerous Iranian proxy army on their border. Indeed, the Saudis have much to learn from Israel’s experience. Even with the most sophisticated weapons, it is all but impossible to defeat a militia that is well entrenched in a civilian population. The stronger side is blamed for the pain of those civilians. For the weaker lot, survival is victory.
So, even though the Houthis are partially responsible for starting the war and capable of great cruelty, it is the Saudis who are accused of war crimes. Often the accusation is justified. In their air campaign, they have been careless and incompetent at best, and probably cynical. Human-rights groups say bombs have been aimed at schools, markets, mosques and hospitals. And the blockade raises suspicion that the Saudis are using food as a tool of war.
The longer the war goes on, the more Saudi Arabia’s Western allies are complicit in its actions. President Donald Trump has given Saudi Arabia carte blanche to act recklessly. He may think it is all part of confronting Iran; or he may want to support the liberalising reforms of the Saudi crown prince, Muhammad bin Salman; or he may hope to profit by selling the Saudis “lots of beautiful military equipment”. Whatever the case, he is damaging America’s interests. Precisely because of the importance of Saudi Arabia—the world’s biggest oil exporter and home to Islam’s two holiest places—the West should urge restraint on the impetuous prince and help disentangle him from an unwinnable war.
How? Peace talks led by the UN have begun with the demand that the Houthis surrender. That is unrealistic. Better to freeze the conflict and find another mediator, such as Oman or Kuwait. A deal should involve a phased withdrawal of Houthi fighters from Sana’a and the Saudi border, and the end of the Saudi blockade. Yemen needs an inclusive government, elections and a new structure for the state. Saudi Arabia will need guarantees that Iranian arms are not flowing into Yemen. Then it will have to cough up the cash to rebuild the country.
None of this will be easy. But a reasonable peace offer is more likely to crack the Houthis than more bombing. Without the cover of fighting Saudi aggression, the Houthis will have to answer for their failures. The public is increasingly turning against them, the alliance with Mr Saleh is fraying and the Houthis themselves are divided.
Stop the war
Right now, far from halting the spread of Iran’s influence, the war has deepened the Houthis’ reliance on Iran, which has an easy and cheap means of tormenting the Saudis. And because Saudi Arabia is bogged down in Yemen, Iran has a freer hand to set the terms of a settlement in Syria. The war is a drain on the Saudis at a time of austerity and wrenching economic reforms at home. They should therefore learn another lesson from Israel’s experience of fighting Hizbullah. If wars are to be fought at all, they should be short, and have limited aims. Deterrence is better than debilitating entanglement.






Comments