Anatole Kaletsky
The opposite of populist nationalism is not globalist elitism; it is economic realism. And in the end, countries such as Britain, the United States, and now Italy will learn the hard way that reality always eventually wins.
Nationalism versus globalism, not populism versus elitism, appears to be this decade’s defining political conflict. Almost wherever we look – at the United States or Italy or Germany or Britain, not to mention China, Russia, and India – an upsurge of national feeling has become the main driving force of political events.
By contrast, the supposed rebellion of “common people” against elites has not been much in evidence. Billionaires have taken over US politics under President Donald Trump; unelected professors run the “populist” Italian government; and all over the world, taxes have been slashed on the ever-rising incomes of financiers, technologists, and corporate managers. Meanwhile, ordinary workers have resigned themselves to the reality that high-quality housing, education, and even health care are hopelessly beyond their reach.
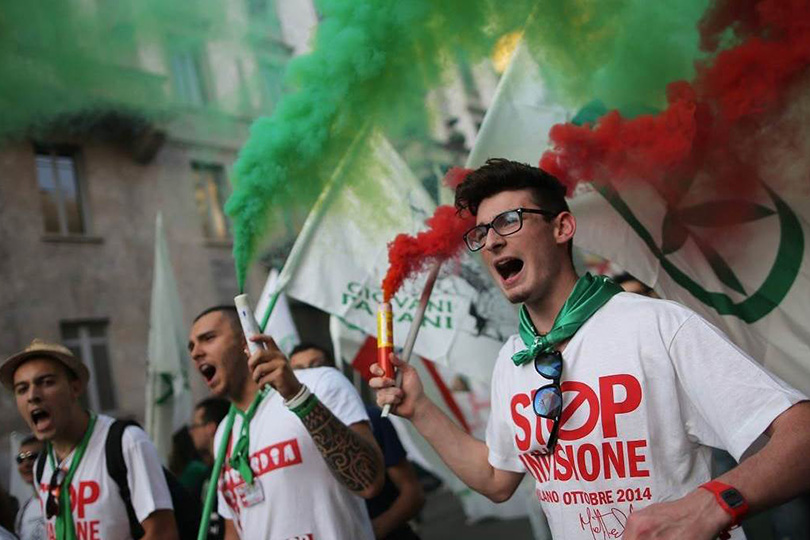
The dominance of nationalism over egalitarianism is particularly striking in Italy and Britain, two countries once famous for their phlegmatic sense of national identity. Flags in Britain are notable for their absence even on government buildings, and until the Brexit referendum the people there were so relaxed about their nationhood that they could not even be bothered to agree on the country’s name: the United Kingdom, Britain, or England, Wales, and Scotland.
Italians were even less nationalistic. Since the European Union’s founding, Italians have been the biggest proponents of federalism, with opinion polls showing that, until recently, voters had more trust in EU leaders in Brussels than in their own government in Rome. Italians are passionate about their culture, history, food, and football, but their patriotism has mostly been directed to regions and cities, not to the nation state. They prefer to be ruled from Brussels than from Rome.
The far-right League party, the junior member in Italy’s new coalition government, was still called the Northern League until this year. One of its favorite slogans was “Garibaldi did not unite Italy; he divided Africa,” and its main political demand was the country’s abolition. Instead, the party demanded the creation of a new country called Padania that would separate the prosperous northern regions from the corruption and poverty of Rome and points south.
What, then, explains the sudden dominance of nationalism? There is not much positively patriotic about the new nationalism in Italy, Britain, or even the US. Instead, the upsurge of national feeling seems largely a xenophobic phenomenon, as famously defined by the Czech-American sociologist Karl Deutsch: “A nation is a group of people linked together by a common error about their ancestry and a common dislike of their neighbors.” Hard times – low wages, inequality, regional deprivation, and post-crisis austerity – provoke a hunt for scapegoats, and foreigners are always a tempting target.
There is nothing patriotic about Trump’s belligerence against Mexican immigrants and Canadian imports, or the nativist policies of the new Italian government, or Theresa May’s most famous statement after becoming UK Prime Minister: “If you believe you are a citizen of the world, you are a citizen of nowhere. You don’t understand what citizenship means.”
Now for some good news for those of us still proud to be “citizens of the world”: The xenophobic effort to blame economic hardship on foreigners is doomed to failure.
Consider the post-crisis effort to divert popular anger about the collapse of market fundamentalist economics onto “greedy bankers.” This ultimately failed, in part because bankers have huge resources to defend themselves, which foreigners generally do not. But banker-bashing failed to assuage public anger mainly because attacking finance did nothing to boost wages, diminish inequality, or reverse social neglect. The same will be true of the current attacks on foreign influence, whether through immigration or trade.
Britain, for example, is gradually waking up to the fact that European issues have nothing to do with the genuine political grievances that motivated a large part of the “Leave” vote. Instead, the Brexit negotiations will now dominate and distract British politics for many years, or even decades. And Britain’s nationalist confrontation with the rest of Europe will offer politicians of all parties endless excuses for failing to improve everyday life.
In the months or years ahead, voters in the US and Italy will learn the same lesson. There, too, scapegoating foreign influences, whether through trade or immigration, will do nothing to lift living standards or address the sources of political discontent.
Italy has legitimate grievances against the EU: hypocritical and inequitable policies on asylum and sea rescues, self-defeating fiscal rules, and economically illiterate financial policies. But the new government is also exploiting the nationalist upsurge to attack reforms that have nothing to do with Europe and are vital to Italy’s economic success.
Successive Italian governments since the financial crisis have gradually laid the foundations for pension, labor market, and banking reforms. These changes have created the conditions for economic recovery, which began last year, following a decade of recession; but they have been politically unpopular and are now being denounced as symbols of elitist foreign oppression. If the new government abandons all three reform projects, Italians can also abandon hope of economic recovery, perhaps for another decade.
The US will also discover that attacking foreign interests is no panacea and can make hardship worse. Trump thinks his measures against imports from China, Germany, and Canada will hurt these trading partners and create American jobs. This might have been true when the US economy was suffering weak growth and deflation. But in a world of strong demand and rising inflation, German and Chinese exporters will find new markets for their products, whereas US manufacturers will struggle to replace foreign suppliers. BMW and Huawei will be just fine, whereas tariffs will act as a tax on American consumers, through higher prices, and on American workers, businesses, and homeowners, through rising interest rates.
The opposite of populist nationalism is not globalist elitism; it is economic realism. And in the end, reality will win






Comments